FMEA Methodology
- Failure Mode Avoidance (FMA) & Failure Prevention Analysis (FPA)
- Team Structure and rules for efficiency – Cross Functional Team (CFT)
FMEA Development must also use past data that may include both success and failure. This data is the basis for possible Failure Modes and Causes from Eight Disciplines for Problem Solving (8D) or Occurrence Rankings.
Three Path Model
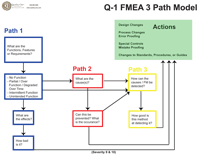
The Three Path Model for vertical FMEA development is a method which organizes teams and activities around failure modes and severities. It is important to look for a defined method in the FMEA training. Working across the page (horizontally) is inappropriate and inefficient. Teaching the form column by column alone does not provide the participant with any proficiency.
- Path 1
- Functions / Failure Modes / Effects of Failure / Severity
- Severity Ranking Guidelines
- Actions for High Severity (9 and 10)
- Path 2
- Causes / Prevention Controls / Occurrence
- Occurrence Ranking Guidelines
- Inputs to Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
- Actions to eliminate and / or reduce cause probability
- Path 3
- Test and Verification Methods
- Detection Ranking Guidelines
- Links to DVP&R
- Actions to improve tests and verification techniques
- Risk Priority Number (RPN)
Knowledge of the FMEA form is not the most useful information that should be acquired. The three primary numbers in an FMEA are Severity, Occurrence and Detection and are linked to each other using combinations of rankings. The Risk Priority Number (RPN) is not the best or only score used for ranking risk. Any FMEA Training course describing that actions should be taken based on the RPN is not following the directives of the FMEA method.
The FMEA is a hub where information is transferred to various responsibilities for action and closure:
- Design FMEA links to Process FMEA
- Actions to reduce design risk
- Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) tools
- Test plans or Design Verification Plan and Reports (DVP&R)